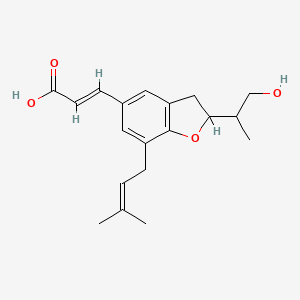
What is artepillin C?
Artepillin C is a phenolic compound, a derivative of p-coumaric acid. It is one of the most important substances found in the world-famous Brazilian green propolis. It is a component of the resin of the South American plant with the Latin name Baccharis dracunculifolia, which resin is collected by bees in the process of producing green propolis. Numerous studies have shown that both B. dracunculifolia, green propolis, and artepillin C itself exhibit the same medicinal properties.
The pharmacological activity of Artepillin C is quite broad and includes:
antioxidant (anti-oxidative),
antimicrobial,
anti-inflammatory,
antidiabetic,
neuroprotective,
gastroprotective,
immunomodulatory, and
anticancer effects.
Most studies focus on antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory effects, combating diabetes, and cancer. These studies have been conducted using both in vitro and in vivo methods.
The mechanisms underlying the anticancer properties of artepillin C include: induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and inhibition of the PAK1 enzyme (p21-activated kinase 1) – a protein characteristic of many human diseases, especially cancerous ones, but also for COVID-19.
Sources:
Hołderna-Kędzia E, Kędzia B. Przeciwnowotworowe działanie składników propolisu. Cz. III. Post Fitoter 2021
Bhargava P, Mahanta D, Kaul A, Ishida Y, Terao K, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC. Experimental Evidence for Therapeutic Potentials of Propolis. Nutrients. 2021
Shahinozzaman M, Basak B, Emran R, Rozario P, Obanda DN. Artepillin C: A comprehensive review of its chemistry, bioavailability, and pharmacological properties. Fitoterapia. 2020
Messerli SM, Ahn MR, Kunimasa K, Yanagihara M, Tatefuji T, Hashimoto K, Mautner V, Uto Y, Hori H, Kumazawa S, Kaji K, Ohta T, Maruta H. Artepillin C (ARC) in Brazilian green propolis selectively blocks oncogenic PAK1 signaling and suppresses the growth of NF tumors in mice. Phytother Res. 2009
We invite you to watch the recording.
Muchas gracias. ?Como puedo iniciar sesion?
Lamentablemente, todavía no tenemos un sitio web, por lo que le invitamos a contactarnos por correo electrónico: biuro@prokit.pl.